This website uses cookies to provide you with a more responsive and personalized service. By clicking “Accept,” you agree to the use of cookies on this website. Please read our Cookie Policy and Privacy Policy for more information on the use of cookies on this website.
GlycogenGlycogen is a form of glucose that is stored in the body and broken down to be used for energy when it’s needed. storage disease type Ia (GSDIa) is a genetic metabolicMetabolic refers to anything related to the chemical changes that take place inside of cells when the body creates energy or other building blocks of life. disease that a person is born with and that affects how the body stores and uses glucoseGlucose is the sugar that the body uses for energy. for energy. Because current approaches to management do not address the root cause of GSDIa, the body is still unable to release glucose, which can trigger hypoglycemiaHypoglycemia is a condition that occurs when there is too little glucose in the bloodstream. and cause damage over time.
Understand the Complications of GSDIa
GSDIa is a rare genetic metabolic disease that can cause complications throughout the body and lead to significant damage over time. When thinking about complications related to GSDIa, it’s helpful to break them into 2 categories: immediate and long term.
Immediate Complications
Long-Term Complications
Immediate Complications
Glycemic and Metabolic Instability
The complications of GSDIa are caused by the body’s inability to maintain stable levels of sugars, fats, and acids.
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is the most immediate complication of GSDIa. In GSDIa, the missing
G6PaseG6Pase is an enzyme that is produced by the
G6PC gene. It is essential for both breaking down glycogen into
glucose and creating new glucose. In GSDIa, G6PC gene variants cause
the body to not make enough of the G6Pase enzyme. enzymeAn
enzyme is a protein in your body that helps to speed up chemical
reactions and is essential to keep them working properly.
stops the body from being able to break down glycogen into glucose and
release it into the bloodstream.
When glucose levels are low, individuals may experience:
- Tremors
- Lightheadedness
- Seizures
- Coma
Other Metabolic Complications
Other serious metabolic complications resulting from the missing G6Pase enzyme include elevated levels of:
- Cholesterol, a type of waxy fat-like substance found in the blood and made by the liver
- Triglycerides, a type of fat that can be found in blood
- Lactic acid, a chemical the body makes during metabolism
- Uric acid, a chemical created when the body breaks down food
Long-Term Complications
Impacts Build Up Over Time
Over time, glycemicGlycemic refers to the level of glucose (or sugar) in one’s blood. and metabolic instability can contribute to long-term complications in many parts of the body.
Long-term complications typically include slower growth and development, poor bone health, nutritional deficiencies, and damage to the liver and kidneys.
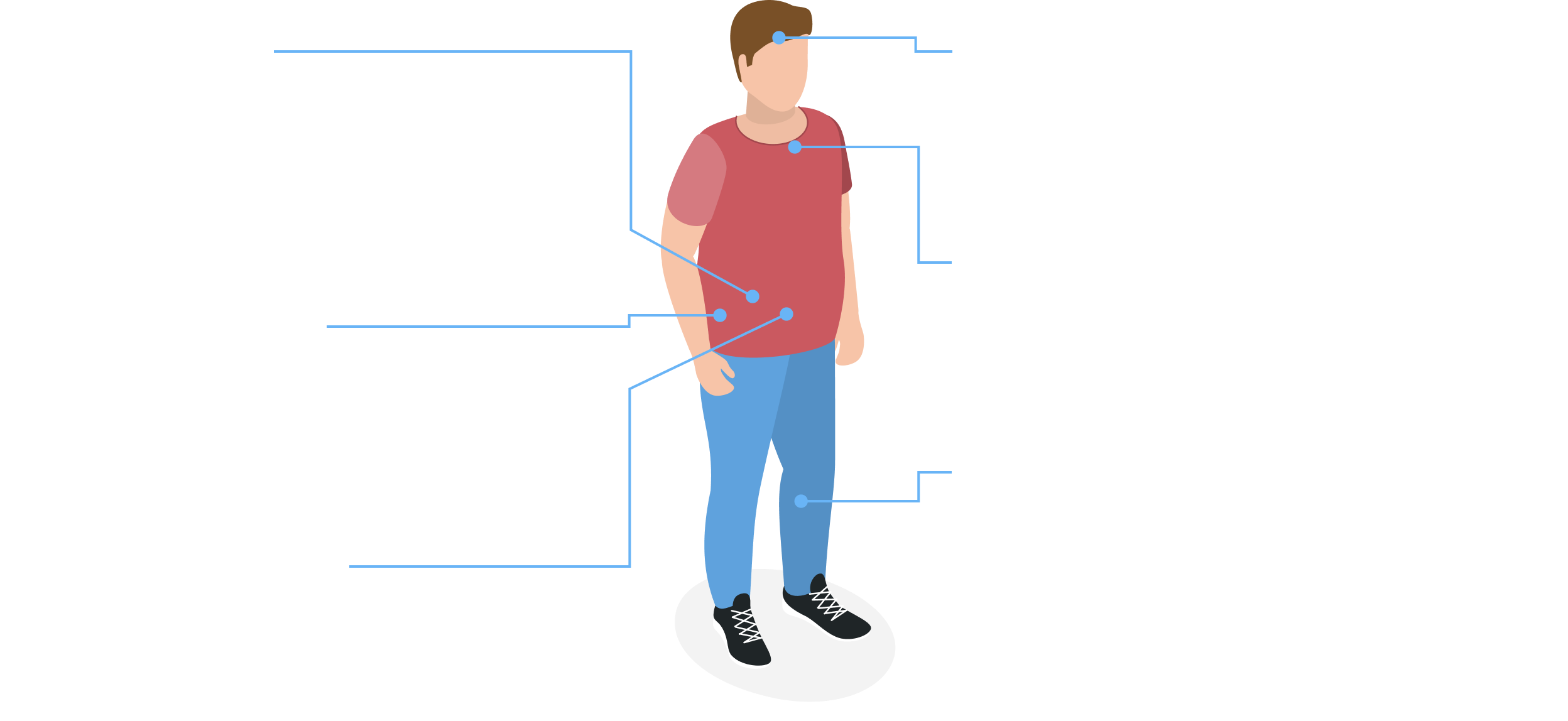
Liver
- Hepatomegaly (enlarged liver)
- Hepatocellular adenomas (liver lesions)
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer)
Kidneys
- Nephromegaly (enlarged kidneys)
- Reduced kidney function
- Chronic kidney disease
- Kidney failure
Intestines
- Bloating
- Diarrhea
Brain
- Cognitive impairment
- Brain damage
Growth and Development
- Delayed growth
- Short stature
Bones
- Osteopenia (low bone density)
- Osteoporosis (weakened bones)
Uncover the Challenges With GSDIa Management
Nutrition
Malnutrition is common due to the restrictive nature of typical GSDIa nutritional plans, potentially affecting growth and development.
Schedule
Strict nutritional management can be difficult to follow, often causing sleep deprivation and anxiety.
Overmanagement
HyperglycemiaHyperglycemia is a condition that occurs when there is too much glucose in the bloodstream. can occur with overmanagement, leading to other problems such as headaches, blurred vision, or fatigue.
Real-World Experiences of Life With GSDIa
Beyond the physical complications, GSDIa can have significant impacts on quality of life. Stories collected from individuals with GSDIa and caregivers reveal the many different parts of their lives that have been affected by the disease.
Emotional Toll
GSDIa can evoke strong feelings of fear, anxiety, grief, and anger. Managing the disease requires constant vigilance, and the risk of hypoglycemia may create significant stress. Overall, living with and managing GSDIa can have a negative impact on a person’s mental health.
Social Limitation
Opportunities to socialize and participate in group activities with peers, such as sleepovers or going out to eat, can be restricted for those with GSDIa due to the challenges of managing the disease.
Daily Burden
Intense feeding schedules mean that days have to be carefully scheduled, limiting the ability to make spontaneous plans. Those who manage GSDIa with a gastric feeding tubeA gastric feeding tube is a tube that can be inserted through the nostril and then down the esophagus to the stomach or can be inserted through the abdominal wall into the stomach to deliver nutrition to the body. may face challenges with participating in activities such as swimming or other sports. Caregivers may have to cut down on work hours to help care for a child with GSDIa.
In Their Own Words
The fatigue, the medical routine, and strict diet illustrate this unique relationship GSD patients and families have with time. We cannot forget the time, never. We are living clocks.
In Their Own Words
My mind never shuts off. My home was between worry and fear 24/7.
In Their Own Words
GSDIa vastly limits your career choices. Physical jobs are almost out of the question, due to my body’s constant demand for food and stable blood sugars.